Rethinking Bitcoin's Lightning Network Design from a Thunderbolt Perspective
 2025-05-26 13:48
2025-05-26 13:481. Why can't I buy coffee with bitcoin?
When most people think of Bitcoin, the first thing that comes to mind is its "decentralized" and "immutable" characteristics. But if you really want to use it to buy a cup of coffee, you will soon encounter an awkward problem: the waiting time for transaction confirmation is even longer than the waiting time for coffee, and sometimes the transaction fee is even higher than the coffee itself. The assets on Bitcoin are still largely "immovable" - most users just hold them; you cannot borrow, combine assets, or interoperate.
The script structure of Bitcoin is extremely conservative, limiting most off-chain interaction scenarios. Its original design goal was not to process tens of thousands of transactions per second. However, the actual demand is right in front of us - people want to be able to use Bitcoin, even if it's just to buy skins or tip video creators, and they don't want to wait ten minutes for it.
2. Lightning Network: a double-edged sword
The Bitcoin mainnet is like a highway, while the Lightning Network is a paid fast channel built next to it. Its core concept is a pragmatic compromise on the throughput limitations of the mainnet: due to the speed bottleneck faced by on-chain transactions, the system no longer insists on recording every transaction on the chain, but allows users to open a dedicated "payment channel" for high-frequency trading, and only settle the final state on the blockchain when the channel is closed. This is similar to friends taking turns to pay the bill and checking out after several outings, rather than transferring money after each meal. The Lightning Network is essentially a network woven from thousands of such payment channels.
However, this seemingly elegant system faces many practical challenges. Firstly, the threshold for channel setting is high - users must lock in funds in advance to establish channels, which means you need to establish a dedicated connection in advance to trade with anyone. Secondly, there is a complex routing problem: if there is a lack of direct channels between user A and user B, even if there are indirect routes like A-C-B, transactions may still fail if the intermediate channel funds are insufficient or the node is unavailable. More seriously, there is a security risk: users must stay online to prevent cheating by submitting expired transactions when closing the channel, which poses unrealistic operational requirements for ordinary users.
Although the Lightning Network has been online for many years, these structural issues have limited its application in the real world. Public data shows that the total value locked in by the Lightning Network is still only about $100 million - a negligible number compared to the trillion-dollar market value of Bitcoin. This has sparked an industry-wide thinking: is it possible to build a better off-chain payment protocol to break through these bottlenecks?
According to ChainCatcher's report on April 15th, HSBC revealed in an official press release that Thunderbolt represents the most significant technological upgrade of Bitcoin in the past decade. Thunderbolt can be seen as "Lightning Network 2.0", but it is not just an upgrade, but also a fundamental redesign of the off-chain interaction paradigm of Bitcoin.
3. What is the Thunderbolt protocol?
Bitcoin Thunderbolt is a soft fork upgrade directly built on the underlying layer of Bitcoin. Unlike layer 2 networks or cross-chain bridge compromises, Thunderbolt introduces protocol-level changes on the Bitcoin mainnet, fundamentally enhancing scalability, transaction performance, and programmability.
Performance layer: Nubit utilizes UTXO bundling technology to significantly optimize Bitcoin's traditional transaction model. Bitcoin's current design processes each UTXO separately, which limits throughput, while UTXO bundling technology can aggregate multiple UTXOs for simultaneous processing. This transaction data compression technology can increase processing speed by nearly 10 times without affecting on-chain security.
Programmability: Thunderbolt reintroduces and extends OP_CAT opcodes - originally present in early Bitcoin versions but later removed. OP_CAT allows for data connections, enabling developers to build more advanced scripting logic and deploy decentralized applications (dApps) directly on the underlying layer of Bitcoin without relying on sidechains, rollups, or cross-chain bridges.
Asset Protocol Layer: Nubit has also introduced a unified token standard called Goldinals, which is based on zero-knowledge proof and state commitment. The framework supports the publication and verification of native Bitcoin tokens without relying on external trust or complex bridging. It integrates fragmented protocols such as BRC-20, Runes, and Ordinals through on-chain automated market makers (BitMM), fully supporting trustless transactions and verification within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Unlike traditional scaling methods such as sidechains, Plasma, Rollups, or asset packaging through bridges, Nubit follows the "native mainnet scaling" path. It integrates solutions such as BitVisa to achieve decentralized identity and credentials. Whether it is transaction compression, smart contract enablement, or on-chain transactions, all functions run directly on the Bitcoin mainnet using native BTC.
3.1 Core Mechanism Analysis
Based on the paper "Stateless Verifiable Execution Layer of Bitcoin Meta Protocol" (Reference 1), Bitcoin Thunderbolt is similar to the Lightning Network and aims to solve the problem of long confirmation time on the Bitcoin mainnet. Although both are committed to improving speed and reducing costs, there are significant differences in their design concepts.
- Lightning Network focuses on payment channels and is only optimized for peer-to-peer transactions. It lacks programmability, involves complex channel setup and maintenance, and has limited scalability.
- Thunderbolt was developed by Nubit and provides a programmable off-chain protocol that can perform Turing-complete operations, supporting the creation of complex stateful assets, liquidity protocols, and financial applications.
Main innovation:
Adjustable multi-party signature
Imagine a Bitcoin signature is divided into two parts: Alice holds one half and the committee holds the other half. Each time the funds are transferred, both parties will add a "key adjustment" - only the new recipient
knows - so they can rebuild the complete signature offline without direct communication.
Asynchronous Committee Ledger:
A group of nodes (such as 4n + 1) maintain ownership consensus. Even if some nodes fail, the system can still operate normally as long as most nodes are online. These nodes cannot transfer funds on their own - they only jointly sign and record ownership, thus maintaining decentralization and security.
Final determination based on atomic exchange
On-chain redemption involves three atomic steps.
1. Alice and the committee spent the original UTXO to transfer the funds to the committee.
2. The committee locks the same amount of funds in a joint vault accessible only to Zenni and the committee.
3. Zenni uses a new two-part signature to complete the exchange.
This process ensures that neither party can cheat or abandon the process.
3.2 Thunderbolt Protocol Design and Technical Highlights
Non-interactive recursion signature delegate:Thunderbolt uses adjustable Schnorr threshold signatures, eliminating multiple rounds of message passing. Only one signature with key adjustment needs to be sent per transmission, significantly reducing communication and uptime requirements.Each jump uses a new locEach transmission will introduce a new key-based signature. The old key will become invalid, preventing signature reuse and enhancing security.Single chain trackingThe only on-chain operation is the initial lock. All subsequent transfers are made off-chain, and the final on-chain redemption is only made at the end of the transaction. Compared with the frequent channel operations of the Lightning Network, Thunderbolt not only improves efficiency but also privacy.Offline elasticityEven if Alice or Zenni is offline, the committee can continue to process redemptions or transfers - without the need for time locking or forced shutdown.Formal verification of security through machine verificationEach key protocol step is formally verified using Tamarin Prover to ensure the security of mathematical verification - not just theoretical promises.
Thunderbolt represents a fundamental rethinking of how Bitcoin supports high-throughput, programmable, and trust-minimized off-chain interactions, while maintaining the core principle of decentralization.
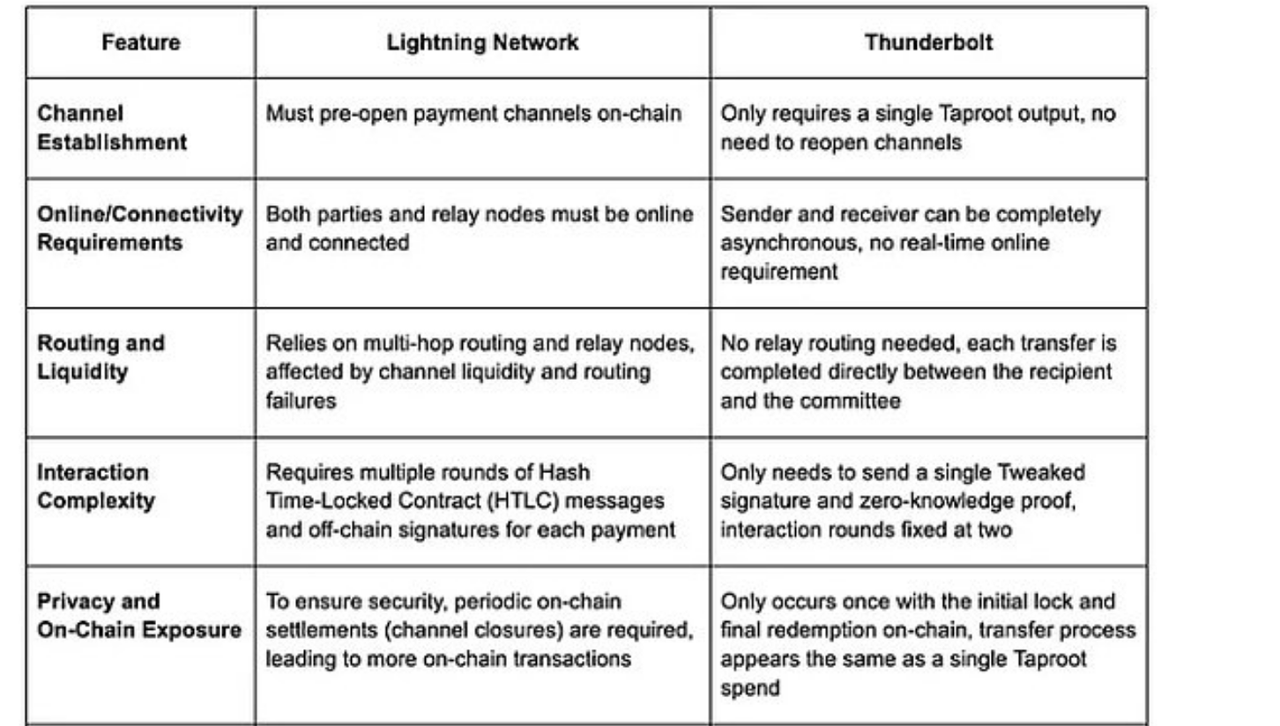
4. How is Thunderbolt different from existing Lightning Network solutions?
Now let's compare Thunderbolt with existing solutions such as BOLT protocol, Breez SDK, and Phoenix to understand the specific improvements it introduces.
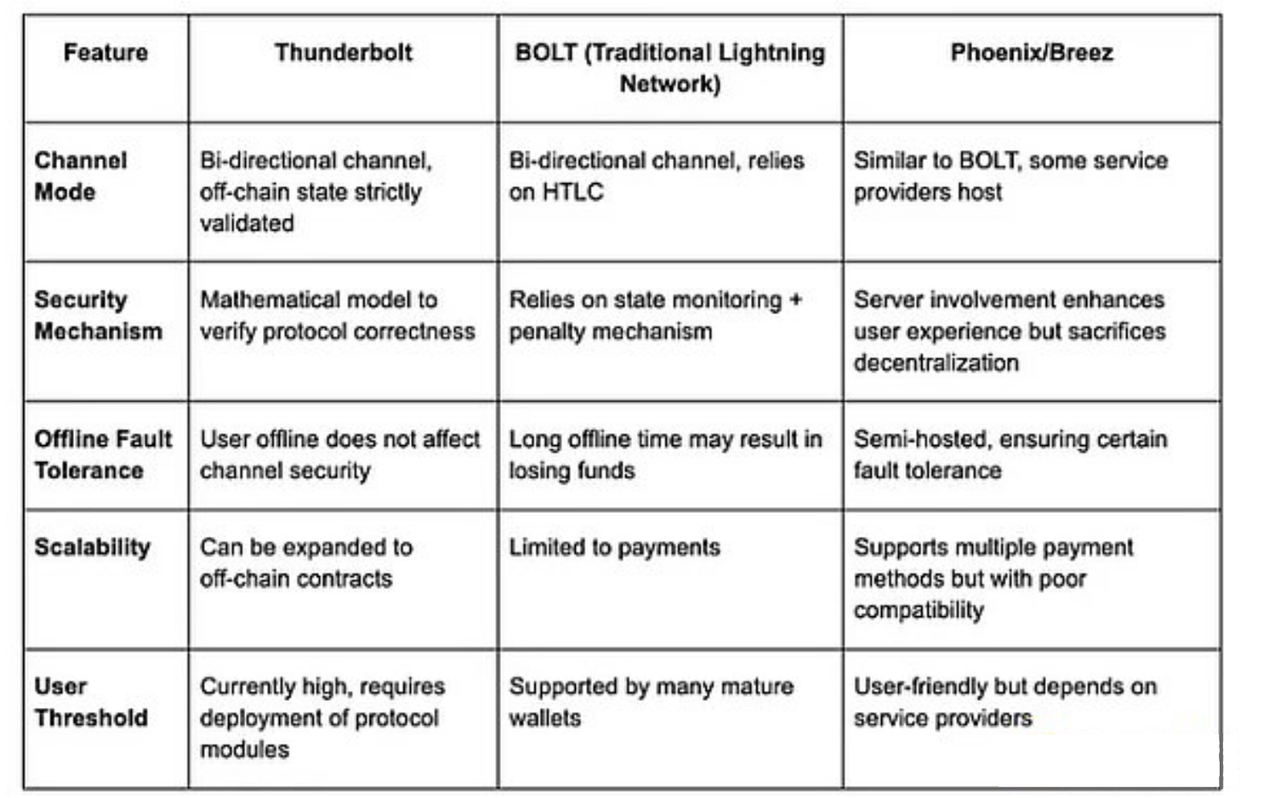
Main differences:
Thunderbolt stands out mainly in terms of security and theoretical soundness. It is one of the few solutions that can claim the following advantages:
- Its protocol design has provable security.
- No malicious user can gain an advantage or value unilaterally.
But it also has obvious shortcomings:
- Deployment complexity: Running Thunderbolt requires a complete protocol stack, which is difficult for ordinary wallet users to adopt.
- Main chain compatibility limitations: Bitcoin's scripting language is extremely limited. Thunderbolt must overcome these limitations, which increases the complexity of implementation.
- Lack of ecosystem support: Unlike BOLT, which has numerous wallets and node support, Thunderbolt is still in the early stages of development.
5. The potential impact of Thunderbolt: A catalyst for BTCFi?
So is Thunderbolt the best solution for BTCFi? A bold but wise view may be:
In theory, Thunderbolt is the best solution for BTCFi, but in practice, it is still in the alpha stage - just like the initial 2.0 white paper of Ethereum: visionary but not yet ready for large-scale production deployment. Based on current observations, the development of Thunderbolt may follow the following three potential paths.
(1) Rollup layer integration: Bitcoin Layer2's DeFi engine
Given the limited scalability of the Bitcoin foundation layer, Thunderbolt can evolve into a Modularization off-chain execution layer in Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions (such as BitVM, Nomic, or BOB). It can be seen as a programmable contract engine embedded in Bitcoin Rollup.
Example:
- BOB may integrate Thunderbolt's payment channels for native BTC transactions.
- The RGB ecosystem can adopt Thunderbolt's state management logic.
- BitVM supports advanced logic and can make Thunderbolt the standard for smart contracts.
- Babylon, Bitlayer, and similar systems can embed Thunderbolt as an off-chain contract execution module.
(2)Build an independent parallel ecosystem
Thunderbolt may follow in the footsteps of the Lightning Network and develop its own infrastructure: nodes, operators, aggregators, and possibly even Thunderbolt-LSP (liquidity service provider). With the support of Nubit and early Bitcoin miners, its soft fork scheme - UTXO bundling and OP_CAT - enables Thunderbolt to natively support protocol assets such as BRC-20, Runes, and Ordinals.
In this case, Thunderbolt can develop into a mature ecosystem with the following characteristics:
- Thunderbolt wallet (similar to Phoenix)
- Thunderbolt nodes (light nodes for channel operations)
- Thunderbolt DEX (off-chain order matching)
- Thunderbolt AMM (off-chain liquidity pool)
(3) Be replaced by simpler solutions
The future of Thunderbolt is still uncertain. It may eventually be replaced by simpler or more efficient alternatives.
- BitVM can provide a more scalable contract execution model.
- Cross-chain ZK technology may make it possible to deploy fully trusted BTC on other chains.
- The new native Bitcoin protocol can unify payments, loans, and contracts into a seamless system.
The real impact: off-chain composability
Thunderbolt's biggest breakthrough is not only in payments, but also in introducing off-chain composability of Bitcoin assets - a concept that is crucial to the DeFi prosperity of Ethereum. The success of Ethereum is due to its integrated development stack: Solidity, Hardhat, Ethers.js, and Metamask. Thunderbolt can also provide a similar foundation for Bitcoin.
Its core innovations - OP_CAT and UTXO Bundling - are particularly exciting:
- OP_CAT achieved Bitcoin's native programmability for the first time.
- UTXO bundles compressed transaction data to enhance on-chain throughput - similar to Ethereum aggregation.
These advances together drive our vision of achieving a unified Bitcoin ecosystem protocol and trustless asset exchange through BitMM - all without the need for bridging or packaging tokens. Nevertheless, Thunderbolt is still closer to a "powerful mathematical paper" than a readily available developer stack.
Latest news
-

- See more
Bitcoin breaks through 110,000 dollars, regrets and misses of those years
On May 22, the 14th anniversary of Bitcoin Pizza Day, Bitcoin broke through the ...
 2025-05-26
2025-05-26
-
- See more
Rethinking Bitcoin's Lightning Network Design from a Thunderbolt Perspective
Why can't I buy coffee with bitcoin?When most people think of Bitcoin, the first...
 2025-05-26
2025-05-26